Google Shopping Ads are a powerful tool for ecommerce businesses, helping products appear at the top of search results with eye-catching visuals, prices, and store names. Unlike traditional text ads, Shopping Ads use high-quality images to attract shoppers and provide key product details at a glance. This makes them highly effective in driving potential customers directly to product pages, increasing sales and brand visibility.
For ecommerce ads, Google Shopping Ads offer several advantages:
- Higher Visibility – Products appear at the top of search results, grabbing attention quickly.
- Better Quality Leads – Shoppers clicking on these ads already have purchase intent.
- Automated Product Targeting – Google matches ads to relevant searches based on product data.
- Higher ROI – Visual product listings lead to better engagement and conversions.
A well-designed Google Shopping Ad can make all the difference between a shopper clicking on your product and scrolling past it. Since Shopping Ads rely heavily on visuals, the quality of your product images, pricing strategy, and ad copy directly influence CTR and conversions.
Quick Teaser: Design Tips to Improve Your Google Shopping Ads
In this blog, we’ll cover essential design strategies to make your Google Shopping Ads stand out and drive more sales, including:
- How to choose the best product images for maximum impact.
- Writing optimized product titles and descriptions that improve search visibility.
- Using pricing strategies and promotions to attract more buyers.
- The importance of customer reviews and trust signals for conversions.
Let’s dive in! 🚀
Understanding Google Shopping Ad Format
Google Shopping Ads are designed to showcase products visually, making them highly engaging for online shoppers. Unlike traditional text ads, these ads display product images, and prices, and store information directly within search results on Google, Facebook ads, or any social media ads. This format helps potential buyers quickly compare options and make informed purchasing decisions.
Breakdown of Google Shopping Ad Components
Each Google Shopping Ad contains several key elements that influence a shopper’s decision:
🖼️ Product Image – The most attention-grabbing part of the ad. High-quality, clear images improve engagement and build trust.
📝 Product Title – A concise and keyword-rich title that helps Google match the ad to relevant searches. It should accurately describe the product and highlight key features.
💲 Price – Shoppers compare prices instantly, so competitive pricing can make a big difference. Displaying discounts or sale prices can further attract buyers.
🏬 Store Name – The business name appears under the ad, helping establish brand recognition and trust.
⭐ Product Ratings & Reviews (if available) – Star ratings and customer reviews boost credibility and influence purchase decisions.
🚚 Shipping Information (if applicable) – Displaying “Free Shipping” or estimated delivery times can encourage more clicks.
Why a Visually Appealing Ad Stands Out in a Competitive Marketplace
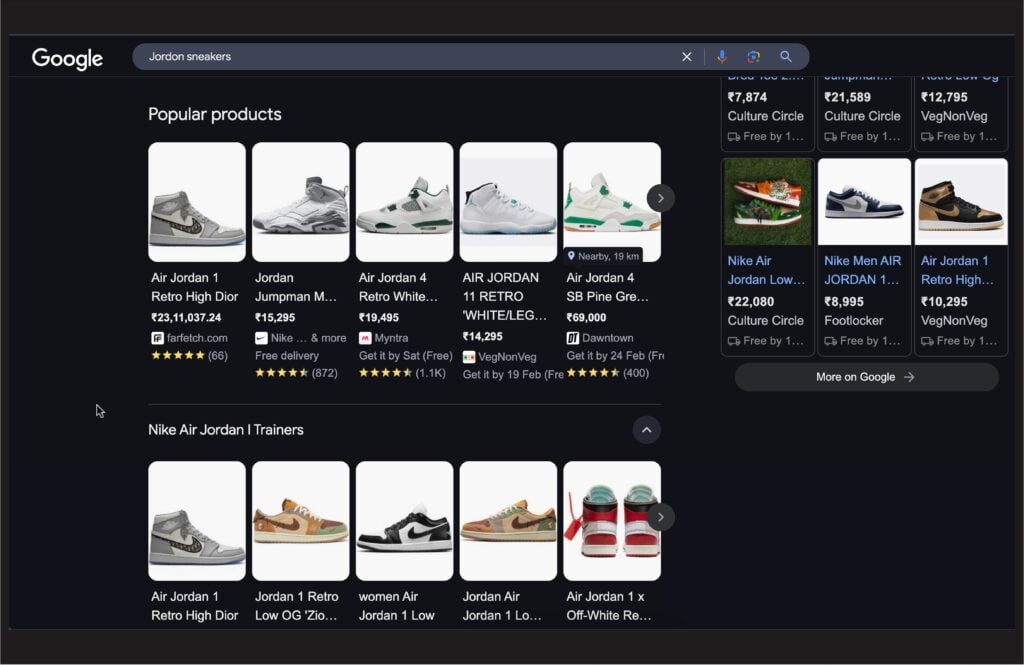
With so many businesses running Google Shopping Ads, a well-designed ad can make all the difference in grabbing attention and driving sales. Here’s why:
- First Impressions Matter – A high-quality product image or an eCommerce video immediately signals professionalism and quality.
- Faster Decision-Making – Shoppers scan images and prices. A clear, visually appealing ad makes it easier for them to choose your product.
- Competitive Edge – In a marketplace where multiple sellers offer similar products, better visuals, competitive pricing, and strong reviews help your ad stand out.
- Higher Click-Through Rates (CTR) – A well-optimized ad with an eye-catching image and compelling product title is more likely to get clicks, leading to increased traffic and conversions.
By understanding how Google Shopping Ads are structured and optimizing each component, you can create compelling ads that attract more buyers and improve your sales performance.
The Basics of Campaign Structure for Google Shopping Ads
Setting up a well-structured Google Shopping campaign is essential for maximizing performance and return on investment (ROI). Google Shopping Ads don’t use traditional keywords; instead, they rely on product data from your Google Merchant Center feed. To ensure your ads are optimized, it’s important to understand the different levels of campaign structure:
1. Campaign Level
The campaign level is the foundation of your Google Shopping Ads setup. This is where you define the budget, bidding strategy, and targeting settings for your entire campaign.
Key Settings at the Campaign Level:
- Budget – Decide how much you want to spend daily on the campaign.
- Bidding Strategy – Choose between manual CPC (cost-per-click) or automated bidding like Maximize Clicks or Target ROAS (Return on Ad Spend).
- Targeting Options – Set location targeting, device preferences, and audience segments.
A well-structured campaign ensures that your budget is allocated efficiently and your ads reach the right audience.
2. Ad Group Level
You create ad groups within a campaign to organize your products into different categories. Each ad group contains one or more product groups, determining how your ads are structured.
Why Ad Groups Matter:
- Help organize products by category, brand, or pricing.
- Allow different bidding strategies for different product types.
- Improve control and reporting, making it easier to analyze performance.
For example, if you’re selling footwear like Nike Shoes, you might have separate ad groups for men’s shoes, women’s shoes, and kids’ shoes. This way, you can track and optimize each category individually.
3. Product Group Level
At the product group level, you divide your inventory into smaller segments based on product attributes. Google Shopping automatically assigns “All Products” as the default product group, but breaking it down further helps improve bidding efficiency and ad relevance.
Ways to Segment Product Groups:
- Category – Organize products by Google’s predefined categories (e.g., Electronics > Smartphones).
- Brand – Target specific brands within your inventory.
- Item ID – Set bids for individual high-performing products.
- Product Type – Group products based on your store’s custom categories.
- Custom Labels – Tag products with unique attributes like “Best Sellers” or “High-Margin Items.”
Properly structured product groups allow advertisers to adjust bids strategically, optimize performance, and improve ROI.
4. Shopping Campaign Priority Levels
If you run multiple Shopping campaigns for the same products, Google uses campaign priority settings to determine which campaign should serve the ad first. There are three priority levels:
- Low Priority – Used for general campaigns or when multiple campaigns are running.
- Medium Priority – Given to more targeted campaigns, such as seasonal promotions.
- High Priority – Reserved for top-performing or high-value products that need maximum visibility.
Example Use Case:
If you have both a holiday sale campaign and a regular Shopping campaign, you can set the holiday sale campaign to High Priority so it takes precedence during the sale period.
Design Tips to Make Your Google Shopping Ads Stand Out
Creating high-performing Google Shopping Ads isn’t just about listing products—it’s about making your ads visually appealing, informative, and optimized for conversions. Here are key design strategies to help your Shopping Ads attract more clicks and drive more sales.
Choose the Right Product Image

The product image is the first thing shoppers notice, making it the most crucial element of your ad. A well-chosen image can significantly impact click-through rates (CTR) and conversions.
- Use high-resolution images – Blurry or pixelated images can make your ad look unprofessional. Ensure your product photos are crisp, clear, and high-quality.
- Showcase the product clearly – Avoid excessive branding, cluttered backgrounds, or distracting elements. Use a plain white or neutral background to keep the focus on the product.
- Use multiple angles or lifestyle images – Showing different angles, zoom-ins, or real-life usage helps shoppers visualize the product better, increasing their likelihood of purchasing.
Optimize Your Product Titles & Descriptions
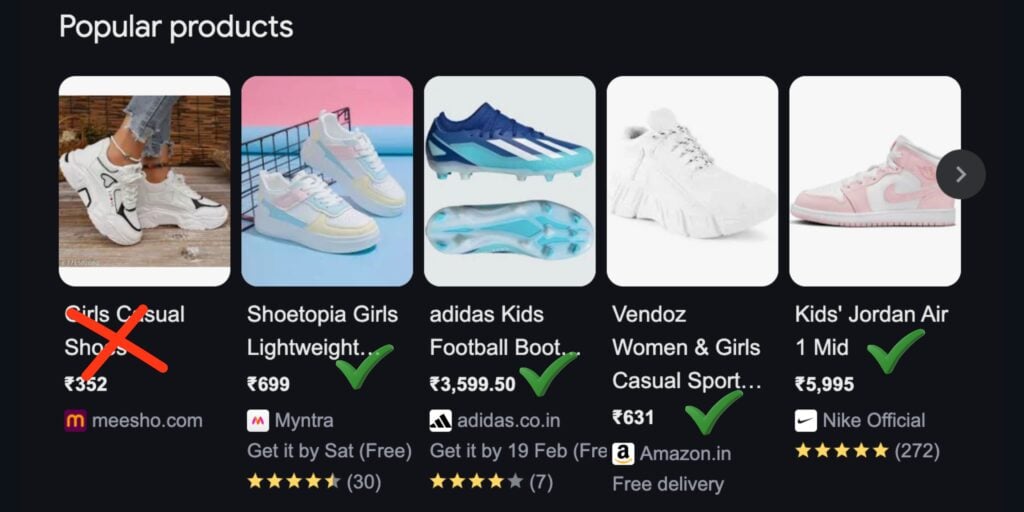
A well-optimized title and description improve ad visibility and ensure Google matches your ad with relevant searches.
- Keep titles short, keyword-rich, and informative – Include essential product details like brand, color, size, and model while keeping it easy to read.
- Highlight key product attributes in the first few words – Since Google may truncate long titles, prioritize the most important information at the beginning.
- Avoid unnecessary filler words and excessive capitalization – Titles should be clear and natural, avoiding all caps or clickbait-style wording.
Highlight Competitive Pricing & Promotions
Pricing is one of the biggest factors in a shopper’s decision to click on an ad. If your price isn’t competitive, potential customers may choose a competitor’s listing instead.
- Ensure your pricing is competitive – Maintain good competitor analysis by regularly checking competitor prices and adjusting accordingly to stay attractive in search results.
- Use sale price annotations – If your product is on sale, Google strikes through the original price and highlights the discounted price, increasing urgency and engagement.
- Leverage Google Merchant Promotions – Offer discounts, free shipping, or bundle deals to stand out. Promotions like “10% Off Today” or “Free Shipping on Orders Over $50” can boost clicks.
Use Trust Signals (Ratings & Reviews
Shoppers are more likely to buy from a store they trust. Displaying ratings and reviews can help build credibility and increase conversions.
- Display customer ratings and reviews – Ads with star ratings often get higher CTRs because they signal quality and reliability.
- Encourage customers to leave reviews – More reviews mean stronger social proof. Follow up with buyers and request feedback through post-purchase emails.
- Utilize third-party review platforms – Platforms like Google Customer Reviews, Trustpilot, or Yotpo can help gather verified reviews that appear in your ads.
Ensure Your Ads Are Mobile-Friendly
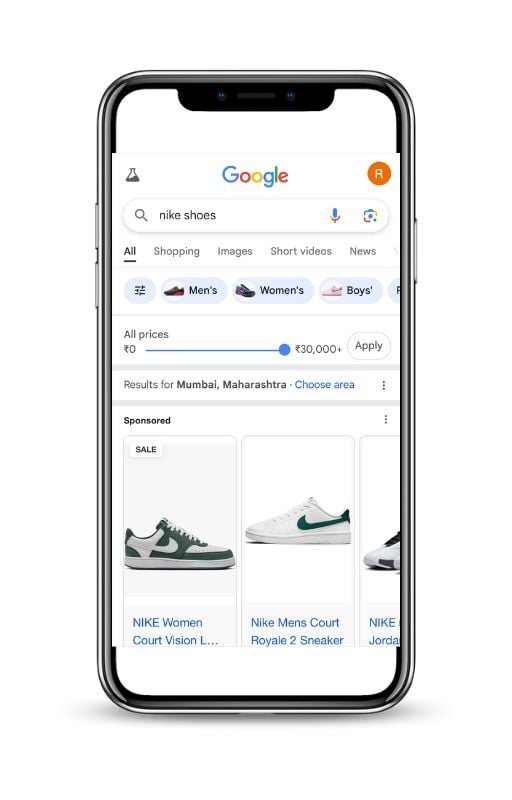
With most online shopping happening on mobile devices, your ads must be optimized for smaller screens.
- Optimize images and text for mobile screens – Ensure product images remain clear and detailed even when viewed on smaller devices.
- Test ad performance across different devices – Regularly check how your ads appear on smartphones, tablets, and desktops to ensure a consistent shopping experience.
- Use responsive images – If possible, use mobile-friendly product images that adapt to different screen sizes without losing clarity.
A/B Test Different Ad Variations
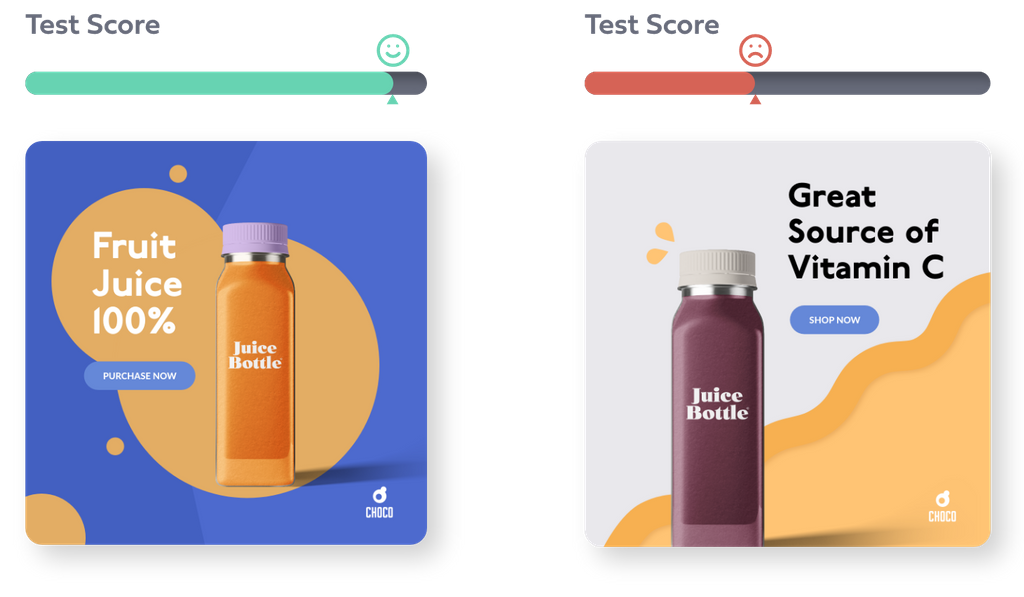
Continuous testing and optimization are key to improving performance and maximizing ad spend efficiency.
- Experiment with different product images, titles, and descriptions – Test which elements perform best in terms of CTR and conversion rates.
- Analyze performance data and adjust accordingly – Use Google Ads reports to track which ads generate the most engagement and sales.
- Continuously refine your ads based on user engagement – If a certain image, title, or promotion is driving better results, apply similar strategies to other products.
Ways Advertisers Set Up Their Google Shopping Campaigns
Setting up a well-structured Google Shopping campaign is essential for maximizing ad performance, increasing visibility, and improving return on investment (ROI). Advertisers use different strategies to organize their campaigns based on factors like product category, pricing, brand, profit margins, and audience targeting. Below are some of the most effective ways advertisers structure their Google Shopping campaigns.
Setting up a well-structured Google Shopping campaign is essential for maximizing ad performance, increasing visibility, and improving return on investment (ROI). Advertisers use different strategies to organize their campaigns based on factors like product category, pricing, brand, profit margins, and audience targeting. Below are some of the most effective ways advertisers structure their Google Shopping campaigns.
1. Segmenting Campaigns by Product Category
Many advertisers structure their Google Shopping campaigns based on product categories to improve targeting and budget control.
Why It Works:
- Ensures better control over bids by grouping similar products.
- Helps analyze performance per category to adjust strategy accordingly.
- Allows advertisers to customize ad copy, promotions, and budget allocation for each category.
Example: A clothing retailer might create separate campaigns for Men’s Wear, Women’s Wear, and Kids’ Clothing to track and optimize performance more effectively.
2. Using Smart Shopping vs. Standard Shopping Campaigns
Advertisers can choose between Standard Shopping Campaigns (manual control) and Smart Shopping Campaigns (automated optimization).
Standard Shopping Campaigns:
- Advertisers manually adjust bids, segment products, and optimize performance.
- Provides more control over targeting and bidding strategies.
- Ideal for businesses that want granular control over their campaigns.
Smart Shopping Campaigns:
- Uses Google’s machine learning to automate bids and ad placements.
- Automatically optimizes for the highest conversions and best ROI.
- Great for advertisers with limited time or resources.
Example: An e-commerce business that wants to maximize automation might use Smart Shopping, while a retailer looking for detailed control over bids and product segmentation would prefer Standard Shopping.
3. Organizing Campaigns by Price Range

Segmenting products by price range ensures that ad spend is distributed efficiently across low-ticket and high-ticket items.
Why It Works:
- Prevents low-margin products from eating up the ad budget.
- Helps advertisers set different bidding strategies based on product value.
- Enables better performance tracking based on pricing tiers.
Example: A tech retailer might create separate campaigns for:
Budget Laptops ($300-$600)
Mid-Range Laptops ($600-$1,200)
Premium Laptops ($1,200+)
Each campaign can have a different bidding strategy, ad budget, and promotion strategy to match consumer expectations.
4. Structuring Campaigns by Brand
For multi-brand retailers, structuring campaigns by brand helps in optimizing ad spend and analyzing brand-specific performance.
Why It Works:
- Allows advertisers to allocate more budget to high-performing brands.
- Helps in brand-specific bidding strategies and promotions.
- Enables better reporting and insights on brand performance.
Example: A retailer selling multiple electronics brands might create individual campaigns for Apple, Samsung, and Dell, setting separate bids based on demand and profit margins.
5. Setting Up Campaigns Based on Profit Margins
Instead of bidding the same for all products, advertisers prioritize high-margin products to maximize ROI.
Why It Works:
- Ensures more ad spend goes toward products with the highest profitability.
- Helps prevent overspending on low-margin items.
- Maximizes return on ad spend (ROAS).
Example: A beauty retailer might separate luxury skincare products (high-margin) from drugstore skincare products (low-margin) and allocate more budget to high-margin items.
6. Location-Based Campaign Structuring
Advertisers running Google Shopping campaigns in multiple regions often separate campaigns by geographic location for better targeting.
Why It Works:
- Helps adjust bids based on demand in different locations.
- Allows for regional promotions (e.g., free shipping in select areas).
- Helps avoid wasted ad spend in low-performing regions.
Example: A furniture store operating nationwide might run separate campaigns for urban areas (high demand, high competition) and rural areas (lower demand, lower competition) with different bidding strategies.
7. Leveraging Audience Targeting for Shopping Campaigns
Using audience segmentation allows advertisers to target specific customer groups based on shopping behavior.
Key Audience Targeting Strategies:
Remarketing Lists for Shopping Ads (RLSA) – Targets past website visitors to encourage conversions.
New vs. Returning Customers – Different ads for first-time buyers vs. loyal customers.
Customer Match – Uses existing customer data (emails) to target repeat buyers.
Example: An online fashion retailer might show exclusive discounts to past customers while offering free shipping to new visitors.
8. Prioritizing Best-Sellers and Seasonal Products
Focusing ad spend on top-performing products and seasonal trends can drive better results.
Why It Works:
- Maximizes visibility for best-selling products that already perform well.
- Helps capitalize on seasonal demand (e.g., Black Friday, Christmas, or Back-to-School sales).
- Ensures high-ROI products receive the most ad spend.
Example: A toy store might run a high-priority campaign for trending holiday toys in December, ensuring they appear first in search results.
Conclusion
Creating a well-structured and visually compelling Google Shopping campaign is key to standing out in a competitive e-commerce landscape. By implementing strategic campaign structures, optimizing product images and AI titles, leveraging audience targeting, and continuously testing ad variations, advertisers can maximize their return on investment (ROI) and drive more sales.
Success with Google Shopping Ads doesn’t happen overnight,it requires continuous testing, monitoring, and optimization. Start by implementing one or two strategies, track the results, and refine your approach based on performance data.
Ready to improve your Shopping Ads? Apply these strategies today and monitor how they impact your ad performance. The more you fine-tune your campaigns, the better your results will be!
Related Posts,
- A Simple Guide on How to Use the Google Ads Transparency Center.